Last updated on March 25, 2021 at 02:38 pm
Oats are healthy & support weight-loss. We want to tell you all about Oats so you understand which one’s you can eat, where they are coming from and what their nutritional values are. Find out which type of oat has the lowest amount of calories and is the most healthy & supports weight-loss.
In most communities around the world, crops are an important determinant that played a pivotal role in its development, human health, and economy. Oat grains have garnered that same respect throughout history.
History of Oats
Oat (plural Oats) have become a staple that most people depend on to build a healthy eating regimen or maintain healthy body weight. As much as this grain is praised, it has a humble beginning that dates back to 2,000 BC.
While no one can say categorically where oat originated from, history traces it back to Greece. Oats was an edible crop in the Mediterranean and Middle East countries before most of the world knew about the grain. As the trade chain of wheat and barley moved, grains of oats entered Europe, Asia, and North America.
Oats were fast-growing grass; they overtook wheat and barley in the field and were treated as a weed by the Europeans. In fact, one story has it that while the Irish and Scottish were making porridge from this grain, the United Kingdom treated it as a weed and fed it to horses.
The dislike for oat dates back to the Roman and Greek empire because of how it took over wheat and barley farms growing taller and sapping the nutrients in the soil.
One reason why oats failed to gain momentum in most European countries was due to the introduction of potatoes. It wasn’t until the 18th century when potatoes became scarce did people begin to see the importance of oat and its similarity and versatility to potatoes.
Oats traveled the world to the USA, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand by British explorers in the 16th to 19th centuries. Today, oats are the most recognized crops in the world, with many health benefits and a barrage of uses more than just food and feeds. Oats are healthy & support weight-loss. And Oat milk is increasingly popular as healthy plant-based milk alternative.
Oats Plant – The Name and Types

Oat is among the oldest grain in the world. The Greeks called it vromi, and the Romans called it Avena. Oats belong to the Gramineae family and cultivated as Avena Sativa. Avena Sativa is the common oats planted and cultivated around the world.
Oats can survive is all climate and soil texture of the world, and even more in temperate regions. Although all oat seeds are edible, only 4 out of the 26 types are utilized. Oats species can be divided into cultivated oats and wilds oats.
Cultivated Oats
- Avena Sativa – which is the common oats we all know as oats. They are grown all over the world and the most versatile grain for all-purpose. These oats are characterized by their pyramid shape seeds with leaves branching out equilaterally. Asides from eating, it has no other tangible importance or use.
- Avena Abyssinica is oats found in Ethiopia and Eritrea, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. It is used mainly as food and to protect the land surface from losing its nutrient. Unlike its cold region counterpart, this hermaphrodite plant is wind-pollinated and does not do well in cold regions. It is planted in June and July and harvested in August through September.
- Avena Nuda is hulless oat. This means the oat is unprocessed and contains all the essential nutrients of a wholesome oat. They are regarded as more nutritious with a higher degree of fiber and other nutrients. This variety of oats is said to grow in the cooler regions of China, Tibet, and its surroundings where it is used as food, feed, and foliage. They are said to migrate from the Orient to Europe, especially to Britain. Rolled oats are an example of hulless oats.
- Avena strigosa – also known as black oats is native to Western Europe and Brazil where it is used for food, feeds, and foliage. This specie grows up to 1.5m in height and has a dense root system. The kernels are plumper and smaller than the Avena Sativa. The plant has a shorter growth cycle with high protein content and nutritional value. It is also known as sand oat, lopsided oat, or bristle oat.
Wild Oats
These are referred to as weeds that grow with other grains. They are capable of damaging the crop, as they grow very fast sapping out needful nutrients from the soil. Commonly known wild oats are:
- Avena fatua is the most common wild known with an immense similarity to the Avena Sativa except its large panicles. This wild oat is a native of Europe and Asia but naturalized in Britain. It is mostly used as feeds for animals.
- The Avena Barbata is a slimmer wild oat with weak steams. These annual grass grow up to 60 cm tall with a flat leaf of 1.5 mm wide.
- The Avena Sterilis or red wild oat is an invasive edible plant that resembles its cultivated cousin, the Avena Byzantina. It is commonly used as animal feeds. Other varieties of wild oats are the Avena Moroccan, Avena Pubescens, Avena Brevis, and Avena Accidentalis.
How is Oat harvested?
Oats is one of the utilized grains in the world, with over 24 million tonnes harvested for food, feed, and other uses annually across the globe. Oats grains are harvested based on when it was planted; two harvesting seasons are spring and autumn. Seeds that are planted in spring will produce a good yield, and better harvest as the plants are unaffected by frost.
Harvesting is done by directly cutting off the heads of the standing plants as soon as the crops ripen. This is then followed by allowing the seeds to dry off completely means ample loss to the farmer. Most farmers harvest the oats when the moisture level is about 12 percent.
The direct heading is a cheaper method of harvesting oats. It allows the oats to maintain its quality and nutritional value even after processing. One disadvantage of oats is it spoils easily by turning rancid. Hence farmers use machines that separate the stem from the plants and then stored in silos until it is reading for processing.
The Processing Steps
- Cleaning and sizing – dirt particles and bad seeds are separated from the good groats.
- Dehulling – when the outer coating is removed from the groats through a centrifugal process. This is used for making the regular oats. Oats that are not hulled are also packed and contain more nutrients than hulled oats.
- Kilning – this is a process when the groats are passed through heat to breakdown the fatty acid contains in oats. As mentioned, oats have a high spoilage rate that causes it to go rancid. This heat treatment stabilizes the grains and stops the enzymatic reaction from taking place.
The oats are then sized, processed further, and packed before heading to kitchen cabinets across the world.
What is the Difference Between Organic and Non-Organic Oats?
How food is grown and processed, classifies it as organic or non-organic. Organic oats are those that are grown without the use of all additives, growth hormones, and/or pesticides.
These are purebred oats without any GMO. Furthermore, all foods, especially grains must undergo some sort of processing. Simple methods like passing through hot water to clean it, do not necessarily affect the nutritional content.
Non-organic oats are oats that were grown using chemicals to hasten the process or quality within a short time frame. These oats also have additives or preservatives in them to extend their self-life or improve on the taste, look, or texture.
Overall, organic oats are better and healthier, so check all labels before buying your favorite brand.
Why are Oats Healthy & Support Weight-Loss?
In the USA, oats received their first FDA approval as a heart-healthy food because of their ability to lower the risk of heart-related diseases. Oats also have a unique antioxidant called avenanthramides that helps reduce inflammation of the blood vessels from the damaging effect of bad cholesterol.
Furthermore, it contains a variety of vitamins and minerals like vitamin B-complex that help in the formation of red and white blood cells. Minerals in oats are calcium, zinc, iron, magnesium, and others to keep you and your cells healthy.
So what are the other reasons you should add oats to your regular meal?
- They are low in bad fat but high in good fats. This makes them one of the best ways to start our day. Oats have a low glycemic index that helps regulate blood sugar and increases metabolism. This reason also makes oat a great way to lose or maintain weight and keep blood sugar low in diabetics.
- Lower cholesterol – the high fiber and beta-glucan in oats helps cholesterol level low and reduce the risk of heart disease. The beta-glucan is also a dietary fermentable fiber that helps prevent colon cancer.
- Keeps you full for long – if you are looking to lose weight, add oats to your diet. Oats are complex carbs that gradually release their energy after eating, preventing unnecessary cravings and binging after meals.
Did you know that half a cup of dry oats contains 150 calories, 6 grams of protein, 3.7 grams fiber, 25-gram carbs, and 2 grams of fat? This same quantity cooked with water just has 170 calories.
Different types of Oats
Steel Cut Oats
Also known as Irish oats, it is made from thick oats groats that were cut with steel blades during the sizing process. They are the healthiest oats containing all the nutritional goodness of raw oats with high protein and fiber for the body. It also have an earthy taste and chewy too.
The fiber in steel-cut oats is insoluble and takes a long time for the body to break it down, keeping you full for long periods. Steel-cut oats are less processed oats hence very healthy. They are not the best for baking because of their rough texture. The best way to eat is to make a traditional porridge, and add fruits or sweeteners as desires.
Rolled Oats
Also called old fashioned oats, these are made by heating and flattening the oats kernels between two rollers before been cut. Rolled oats are thin, flaky, light, and cook fast within 10 minutes. The processing method gives them a long shelf life. Unlike steel oats, they have a higher carb content, high GI, and digest faster after eating.
Using rolled oats for weight loss stalls the fat burning process, and you might not see any immediate change. To get them to bring out their flavors, they make great overnight breakfast oatmeal.
However, in the 1910, the Nagel Brothers were the first to invent rolled oats without steaming the oats. This retained the nutritional value of the oats and as good as steel-cut oats.
Scottish Oats
These are the next best oats with high nutritional value after steel oats. They are also known as porridge oats or quick oats and are more creamy and tastier than other oats. If you do not have access to steel oats, this pinhead shape fine grain is the best even though they do not offer the fullness of steel-cut oats. Scottish oats are great for baking and cooking.
Instant Oat
This is the most common and processed oat on the market. Like rolled oats, they have been rolled thinner give they a very light, flaky, and almost powdery look and feel. An example of instant oat is the infamous Quaker Oat. This oat is easy to cook, takes well to different flavors and the soaking liquid.
Although they have the lowest fiber content, it makes a satisfying meal when paired with the right supplements like chia, nuts, and seeds to boost their fiber value.
Oat Flour
Made from ground oats to powder, they are not the best for baking bread but do excellently well in cookies, pancakes, and others.
Oat Bran
As the name Oat Bran implies, it is the coating of the oat groats. The exterior cover, the chaff, but like most parts of the oat plant, it is super useful and an excellent addition to your meal.
The bran consists of the raw unprocessed oat, which makes is highly nutritious, full of fiber, and protein with fewer carbs. It has a nutty flavor like steel-cut oats. Although termed inedible, the soluble fiber is the perfect way to add texture to your meal and stay full for long. It is a great addition to baking, casseroles, stews, and porridges.
The best oat is STEEL CUT OATS. They are less processed, contain higher fiber, and still maintain nutritional integrity. Although they take the longest to cook, they are delicious and pair well with a variety of fruits and syrups.
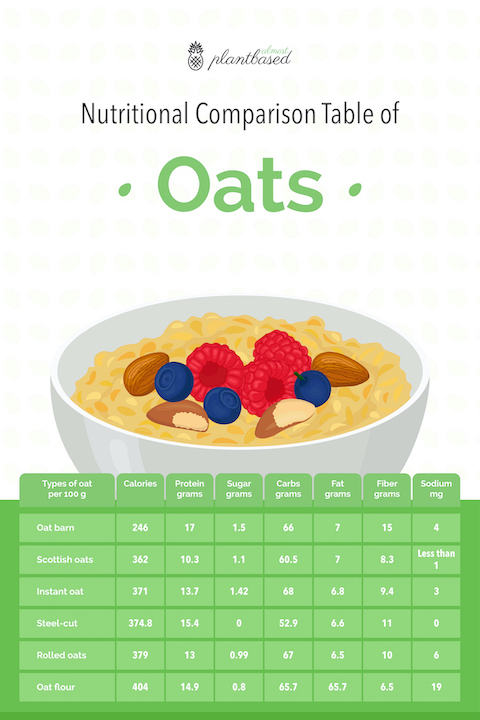
Nutritional Comparison Table of Different Oats
What Type of Oat is the Most Healthy & Supports Weight-Loss?
The Bottom Line
Oats have come a long way, journeying around the world and changing the way we see grains. These super healthy grains have garnered all the respect and accolade they deserve because of their nutritional properties.
Whether you love oats because you want to lose weight with our 21 day weight-loss plan, or you are looking to start eating healthy, there is no better place to start than with a bowl of cooked or raw oats.
Start your day healthy, start your day right, with a bowl of oats!

Leave a Reply